北美数据科学SQL面经(窗口函数)
北美数据科学SQL面经(窗口函数)窗口函数系列1. What are window functions in MySQL?2. How do you define a window function in MySQL?3. What is the difference between aggregate functions and window functions? 4. What is the purpose of the OVER clause in a window function?5. Explain the ROWS and RANGE clauses in the window function6. What are the commonly used window functions in MySQL?7. How do you calculate the cumulative sum/product/subtract/division using a window function?实现累加实现累减实现累乘实现累除8. How can you find the top N records based on a specific column using a window function?9. How do you calculate the moving average using a window function?10. Can you use a window function in the WHERE clause of a query?11. Explain the PARTITION BY clause in a window function.12. How do you handle NULL values when using window functions?13. What is the difference between RANK, DENSE_RANK, and ROW_NUMBER functions?14. Can you give an example of using the LEAD and LAG functions in MySQL?15. How do you use the NTILE function to divide data into equal-sized buckets?FRAME ClauseWhat is the FRAME clause in SQL?How does the FRAME clause work?What are the different types of frame units in SQL?What are the different frame options in SQL?How do you use the FRAME clause in SQL?What is the difference between ROWS and RANGE frame units?Can you use the FRAME clause without specifying the frame start and end?How can you handle ties or equal values when using the FRAME clause?Can you use the FRAME clause with all window functions?
窗口函数系列
1. What are window functions in MySQL?
Window functions in MySQL are a type of function that perform calculations across a set of rows called a "window" or "window frame."
Unlike aggregate functions that return a single value for a group of rows, window functions return a value for each row within the window, based on the specified criteria. They allow you to perform calculations that involve multiple rows without grouping the data.
2. How do you define a window function in MySQL?
1<function_name>(<arguments>) 2 OVER (PARTITION BY <partition_expression> 3 ORDER BY <order_expression> <frame_clause>)Here, <function_name> represents the specific window function you want to use, <arguments> are the parameters passed to the function, <partition_expression> is the expression that defines the partitioning of rows, <order_expression> specifies the order of rows within each partition, and <frame_clause> defines the window frame.
3. What is the difference between aggregate functions and window functions?
The key difference between aggregate functions and window functions is how they handle the result set.
Aggregate functions (such as SUM, COUNT, AVG) collapse multiple rows into a single value, typically by grouping the rows based on specified criteria. They produce a single result for the entire group.
On the other hand, window functions operate on individual rows within a window frame and return a value for each row. They do not collapse rows into a single result. Instead, they provide a way to calculate values based on the ordering and partitioning of the result set, taking into account a specific range of rows.
4. What is the purpose of the OVER clause in a window function?
The OVER clause in a window function is used to define the window or window frame within which the calculation is performed. It specifies the partitioning and ordering of rows for the window function.
PARTITION BY: It divides the result set into partitions or groups based on the specified expression. The window function is applied separately to each partition.
ORDER BY: It defines the order of rows within each partition. The window function is applied in this order to calculate the result.
frame_clause: It specifies the window frame, which determines the range of rows used in the calculation. It can be used to include or exclude specific rows from the window frame.
By using the OVER clause, you can control the scope and boundaries of the window function, allowing you to perform calculations on specific subsets of data within the result set.
5. Explain the ROWS and RANGE clauses in the window function
ROWS clause: The ROWS clause in a window function is used to specify the window frame in terms of a physical number of rows. It allows you to define a fixed range of rows relative to the current row. For example, you can use
ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND 2 FOLLOWINGto include the two rows before and after the current row in the window frame.RANGE clause: The RANGE clause in a window function is used to specify the window frame in terms of logical intervals or values. It allows you to define a range of rows based on the values of the order expression. The RANGE clause is typically used with ordered data and is sensitive to the actual values, rather than the number of rows. For example, you can use
RANGE BETWEEN INTERVAL 1 HOUR PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROWto include rows within one hour before the current row.
6. What are the commonly used window functions in MySQL?
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CUME_DIST() | Cumulative distribution value |
DENSE_RANK() | Rank of current row within its partition, without gaps |
FIRST_VALUE() | Value of argument from first row of window frame |
LAG() | Value of argument from row lagging current row within partition |
LAST_VALUE() | Value of argument from last row of window frame |
LEAD() | Value of argument from row leading current row within partition |
NTH_VALUE() | Value of argument from N-th row of window frame |
NTILE() | Bucket number of current row within its partition. |
PERCENT_RANK() | Percentage rank value |
RANK() | Rank of current row within its partition, with gaps |
ROW_NUMBER() | Number of current row within its partition |
7. How do you calculate the cumulative sum/product/subtract/division using a window function?
x1CREATE TABLE TEST(2 PARENT_ID NUMBER,3 PART_ID NUMBER,4 QUALITY NUMBER);5
6INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(1,1,2);7INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(1,2,3);8INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(1,3,2);9INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(1,4,5);10INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(2,2,3);11INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(2,3,5);12INSERT INTO TEST VALUES(2,4,7);
实现累加
xxxxxxxxxx51SELECT2 T.*,3 SUM(T.QUALITY) OVER (PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID) RUNNING_QUALITY4FROM5 TEST T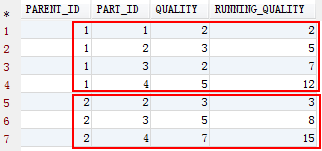
实现累减
xxxxxxxxxx121SELECT2 T.PARENT_ID,3 T.PART_ID,4 T.QUALITY,5 SUM(DECODE(T.RN,1,T.QUALITY,-T.QUALITY)) OVER(PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID) RUNNING_PROD6FROM7 (8 SELECT9 T.*,10 ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID) RN11 FROM12 TEST T) T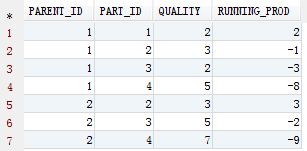
实现累乘
xxxxxxxxxx51SELECT2 T.*,3 ROUND(EXP(SUM(LN(T.QUALITY)) OVER(PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID)),0) RUNNING_PROD4FROM5 TEST T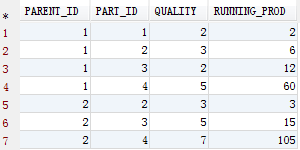
实现累除
xxxxxxxxxx121SELECT2 T.PARENT_ID,3 T.PART_ID,4 T.QUALITY,5 EXP(SUM(DECODE(RN,1,LN(T.QUALITY),-LN(T.QUALITY))) OVER(PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID)) RUNNING_PROD6FROM7 (8 SELECT9 T.*,10 ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY T.PARENT_ID ORDER BY T.PART_ID) RN11 FROM12 TEST T)T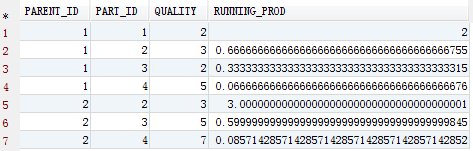
累乘和累除的缺陷是不能对负数进行运算 因为ln(负数)没有意义
8. How can you find the top N records based on a specific column using a window function?
使用子查询和 ORDER BY 子句:
xxxxxxxxxx41SELECT column1, column2, column32FROM your_table3ORDER BY column3 DESC4LIMIT N;在上面的查询中,将结果按照指定列(这里是 column3)降序排序,然后使用 LIMIT 子句选择前 N 行作为结果。
使用子查询和 ROW_NUMBER() 函数:
xxxxxxxxxx61SELECT column1, column2, column32FROM (3SELECT column1, column2, column3, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY column3 DESC) AS row_num4FROM your_table5) AS subquery6WHERE row_num <= N;在上面的查询中,使用 ROW_NUMBER() 函数为每行分配一个行号,根据指定列(这里是 column3)降序排列。然后,在外部查询中筛选行号小于或等于 N 的行。
使用子查询和 RANK() 函数(用于处理并列排名):
xxxxxxxxxx61SELECT column1, column2, column32FROM (3SELECT column1, column2, column3, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY column3 DESC) AS rank4FROM your_table5) AS subquery6WHERE rank <= N;在上面的查询中,使用 RANK() 函数为每行分配一个排名,根据指定列(这里是 column3)降序排列。然后,在外部查询中筛选排名小于或等于 N 的行。
9. How do you calculate the moving average using a window function?
To calculate the moving average using a window function in SQL, you can use the AVG() function along with the ORDER BY and the ROWS or RANGE clause to define the window frame. Here's an example:
efine the window frame. Here's an example:
xxxxxxxxxx41SELECT 2 column1, column2, column3, AVG(column3) 3 OVER (ORDER BY column1 ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS moving_avg4FROM your_table;In the above query, column1 is used to define the order of rows, and column3 is the column for which the moving average is calculated. The AVG() function with the window function syntax calculates the average for each row within the window frame. The window frame is specified using the ROWS BETWEEN clause, which includes the current row and the two preceding rows (2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW).
The result of the query will include the original columns (column1, column2, column3), as well as a new column moving_avg that represents the moving average for each row.
Make sure to replace your_table with the actual table name and adjust the column names according to your specific scenario. Additionally, you can modify the window frame definition to suit your needs, such as using a different number of preceding or following rows or using the RANGE clause instead of ROWS.
10. Can you use a window function in the WHERE clause of a query?
No, you cannot directly use a window function in the WHERE clause of a query. The WHERE clause is evaluated before the window functions are applied in the query execution process.
11. Explain the PARTITION BY clause in a window function.
The PARTITION BY clause in a window function is used to divide the result set into partitions or groups based on one or more columns. It allows you to apply the window function independently within each partition, providing separate calculations or rankings for each partition.
| PARTITION BY | GROUP BY | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Divides the result set into partitions or groups based on specified columns. | Groups the result set into distinct groups based on specified columns. |
| Usage | Used in the context of window functions. | Used with aggregate functions. |
| Aggregation | Performs calculations or evaluations within each partition. | Performs calculations or evaluations across the entire group. |
| Result | Returns all rows from the original table, with additional columns for window function calculations within each partition. | Returns a single row per group, with aggregate function results. |
| Level of Detail | Works at a more granular level within each partition. | Works at a higher level, treating the entire group as a single entity. |
12. How do you handle NULL values when using window functions?
| Window Function Type | Handling of NULL Values |
|---|---|
| Aggregating Functions (e.g., SUM, AVG, COUNT) | NULL values are included in the calculations and treated as 0. |
| Ranking Functions (e.g., ROW_NUMBER, RANK, DENSE_RANK) | NULL values are assigned ranks and considered in the ranking order. |
| Nulls Last/Lowest Ordering | Some window functions allow specifying the placement of NULL values in the ordering. |
| Filtering NULL Values | You can use a WHERE clause within the window function's definition to exclude NULL values from calculations. |
13. What is the difference between RANK, DENSE_RANK, and ROW_NUMBER functions?
| Function | Handles Ties | Generates Rankings |
|---|---|---|
| RANK | Yes | May have gaps |
| DENSE_RANK | Yes | No gaps |
| ROW_NUMBER | No | No gaps |
The table summarizes the key differences between the three functions:
RANK function: It handles ties by assigning the same rank to rows with the same values. However, it may introduce gaps in the ranking sequence.
DENSE_RANK function: It also handles ties by assigning the same rank to rows with the same values, but it does not introduce gaps in the ranking sequence. In other words, the ranks are contiguous.
ROW_NUMBER function: It does not handle ties and assigns a unique incrementing number to each row without any gaps in the ranking sequence.
14. Can you give an example of using the LEAD and LAG functions in MySQL?
下示例数据:
| date | revenue |
|---|---|
| 2022-01-01 | 100 |
| 2022-01-02 | 150 |
| 2022-01-03 | 120 |
| 2022-01-04 | 200 |
In the above example, we use the LAG function to retrieve the previous revenue and the LEAD function to retrieve the next revenue for each row. The LAG and LEAD functions are applied based on the ordering of the dates.
xxxxxxxxxx121200| o2180| |3160| |4140| |5120| o |6100| o | |780| | | |860| | | |940| | | o1020| | |110|__|______|__|_______122022-01-01 2022-01-02
xxxxxxxxxx21Legend:2o - Revenue
LEAD和LAG函数的运作过程
LAG函数的实现示意图:
xxxxxxxxxx61 +---+---+---+---+---+---+2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |3 +---+---+---+---+---+---+4 | | | | | |5 v v v v v v6 NULL 1 2 3 4 5在上面的示意图中,我们有一列数字(1到6)。使用LAG函数,我们可以将每个数字向前偏移一行,从而得到一个新的列。第一行为NULL,因为没有前一行。
LEAD函数的实现示意图:
xxxxxxxxxx61 +---+---+---+---+---+---+2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |3 +---+---+---+---+---+---+4 | | | | | |5 v v v v v v6 2 3 4 5 6 NULL在上面的示意图中,我们有一列数字(1到6)。使用LEAD函数,我们可以将每个数字向后偏移一行,从而得到一个新的列。最后一行为NULL,因为没有后一行。
参数介绍
LAG(expression, offset, default_value)
expression: 需要获取前一行值的表达式或列名。
offset: 指定偏移的行数,表示要获取前几行的值,默认为1,即前一行的值。
default_value: 可选参数,用于指定当偏移行数不可用时使用的默认值。如果不提供默认值,偏移行数不可用时会返回NULL。
xxxxxxxxxx51SELECT2 date,3 revenue,4 LAG(revenue, 1, 0) OVER (ORDER BY date) AS previous_revenue5FROM sales;在上面的例子中,我们通过指定偏移参数为1来获取前一行的revenue值,并将默认值设置为0。如果第一行没有前一行可用,则会返回默认值0。
lead同理
15. How do you use the NTILE function to divide data into equal-sized buckets?
The NTILE function in MySQL is used to divide data into equal-sized buckets or groups. It assigns a bucket number to each row based on the specified number of buckets.
假设有一个名为students的表,其中包含两列:name和score,表示学生的姓名和分数。现在我们希望将这些学生按照分数均匀地分为4个桶。
xxxxxxxxxx51SELECT2 name,3 score,4 NTILE(4) OVER (ORDER BY score) AS bucket_number5FROM students;例如,假设students表中有以下数据:
xxxxxxxxxx121+-------+-------+2| name | score |3+-------+-------+4| John | 80 |5| Mary | 85 |6| Bob | 75 |7| Alice | 90 |8| Mark | 88 |9| Emma | 92 |10| Jack | 78 |11| Kate | 82 |12+-------+-------+
使用上述NTILE查询后,结果将类似于以下表格:
xxxxxxxxxx121+-------+-------+---------------+2| name | score | bucket_number |3+-------+-------+---------------+4| Bob | 75 | 1 |5| Jack | 78 | 1 |6| John | 80 | 2 |7| Kate | 82 | 2 |8| Mary | 85 | 3 |9| Mark | 88 | 3 |10| Alice | 90 | 4 |11| Emma | 92 | 4 |12+-------+-------+---------------+
根据学生的分数,我们将它们均匀地分为4个桶,每个桶中包含2个学生。每个学生都被分配了一个桶号。
FRAME Clause
What is the FRAME clause in SQL?
The FRAME clause is a part of the window function syntax in SQL. It allows you to define the subset of rows within a window frame that the window function operates on. The FRAME clause specifies the starting and ending points of the frame relative to the current row.
How does the FRAME clause work?
The FRAME clause consists of two components: the frame start and the frame end. These components define the range of rows to be included in the window frame. The frame start and end can be specified using different units such as ROWS, RANGE, or GROUPS.
What are the different types of frame units in SQL?
In SQL, there are three types of frame units that can be used with the FRAME clause:
ROWS: Specifies the number of rows before and after the current row to include in the frame.
RANGE: Specifies the logical range of values before and after the current row to include in the frame.
GROUPS: Specifies the number of peer groups before and after the current row to include in the frame.
What are the different frame options in SQL?
In addition to the frame units, the FRAME clause allows you to specify different frame options to further define the frame boundaries:
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING: Indicates that the frame starts from the first row of the partition.
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING: Indicates that the frame ends at the last row of the partition.
CURRENT ROW: Indicates that the frame includes only the current row.
n PRECEDING: Specifies the number of rows or groups before the current row to include in the frame.
n FOLLOWING: Specifies the number of rows or groups after the current row to include in the frame.
How do you use the FRAME clause in SQL?
To use the FRAME clause, you need to include it within the definition of a window function. Here's an example:
xxxxxxxxxx41SELECT 2 column1, column2, SUM(column3) 3 OVER (PARTITION BY column1 ORDER BY column2 ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING) AS sum_column4FROM table_name;In this example, the FRAME clause is specified after the ORDER BY clause and defines a frame of one row before and one row after the current row.
What is the difference between ROWS and RANGE frame units?
The ROWS frame unit operates based on the physical position of rows, while the RANGE frame unit operates based on the logical value of the data. ROWS frame unit includes a fixed number of rows before and after the current row, while RANGE frame unit includes rows that have values within a specified range relative to the current row.
Can you use the FRAME clause without specifying the frame start and end?
Yes, you can use the FRAME clause without specifying the frame start and end. In such cases, the default frame boundaries are used, which is equivalent to the entire partition. This means that the window function operates on all rows within the partition.
How can you handle ties or equal values when using the FRAME clause?
When using the FRAME clause, ties or equal values can be handled by specifying the appropriate frame unit and frame options. For example, if you want to include all rows with equal values in the frame, you can use the RANGE frame unit with UNBOUNDED PRECEDING and UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING options.
Can you use the FRAME clause with all window functions?
No, the availability and compatibility of the FRAME clause depend on the specific window function being used. Some window functions may not support the FRAME clause or may have restrictions on the frame units and options that can be used. It's important to refer to the documentation of the specific database management system and window